Matcha improves sleep quality, social cognition, researchers say, and you don’t need to drink it

Results of year-long clinical trial give us more reasons than ever to drink, or eat, matcha.
Japan has loved matcha for centuries, and with its recent rise to stardom as a dessert flavor, it’s arguably more popular than ever. So green tea fans will be happy to hear that new research suggests matcha doesn’t just taste good, but is good for you in some very important ways.
Tea producer Itoen and MCBI, a medical research firm established by the University of Tsukuba, recently announced the results of a year-long clinical trial investigating the effects of a sustained daily intake of matcha. Starting with a group of 939 men and women between the ages of 60 and 85, 99 were diagnosed with either mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or subjective cognitive decline (SCD). Those 99 then took part in a year-long trial in which the target group consumed matcha every day for 12 months, while the control group was given placebos.
The participants underwent cognitive function and sleep quality evaluations, as well as various blood and neuroimaging tests, at the start and end of the trial, which the researchers describe as a double blind placebo-controlled randomized comparative study. At the end of the year, the matcha group, compared to the placebo group, displayed “a significant improvement in social cognition assessed with a facial expression recognition test, specifically, the precision of their perception of emotions based on facial expression.”
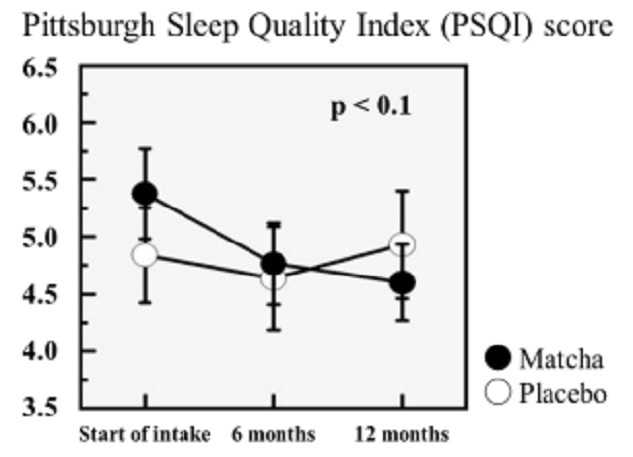
In addition, the matcha group showed an improvement in their quality of sleep. This was determined using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, a self-report questionnaire protocol in which a lower numerical score is indicative of better sleep.
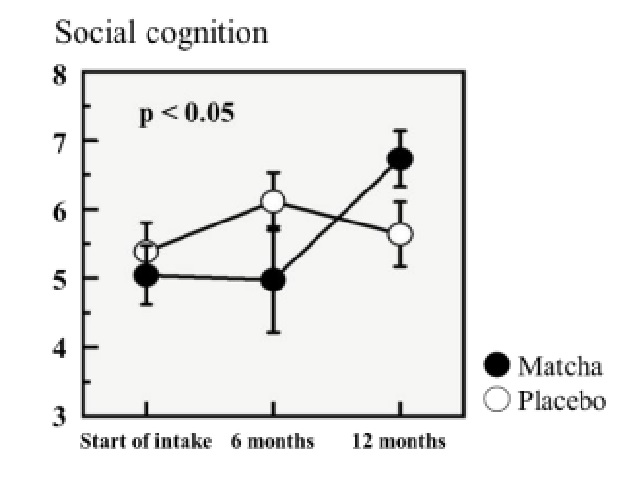
What’s especially interesting about the study is the manner in which the matcha was consumed. Each day, the matcha group consumed two grams of matcha, which is the average amount found in a cup of matcha green tea. However, the matcha was administered in capsule form. This would imply that the improvements the matcha group experienced weren’t the results of extra time spent relaxing or in quiet self-reflection while leisurely sipping a cup of tea, but were from the matcha itself, which in turn suggests that maybe the same benefits could be experienced from eating matcha sweets.
▼ The placebo group was given colored corn starch capsules, and so sadly the study provides no similar medical justification for also eating non-matcha candy.

The results of the study were presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference, held this month in San Diego, and while the matcha and control groups displayed no significant differences in other neuropsychological tests, the prospect of better sleep really means we’re now entirely out of reasons not to eat matcha ice cream for dessert every night from now on.
Source: Itoen (1, 2) via Shokuhin Sangyo Shimbun via Livedoor News
Top image ©SoraNews24
Insert images: Itoen, Pakutaso
● Want to hear about SoraNews24’s latest articles as soon as they’re published? Follow us on Facebook and Twitter!
Credit:

0 comments:
Post a Comment